Productive Failure
Keywords
Productive Failure, learning design, representations and solution methods (RSMs), complex problem-solving, instructional intervention
Introduction
Productive Failure (PF) is a learning design that entails the design of conditions for learners to persist in generating and exploring representations and solution methods (RSMs) for solving complex, novel problems. Though such a process may initially lead to failure to generate canonical RSMs, it has a hidden efficacy that is germane for learning provided an appropriate form of instructional intervention follows that can consolidate and assemble student-generated RSMs into canonical RSMs.
Research Questions
1. What mechanisms make productive failure an effective learning strategy?
2. How can student-generated representations and solution methods (RSMs) be effectively consolidated into canonical forms?
3. What instructional interventions optimize learning outcomes following productive failure?
State of the Project
Problems with Early Direct Instruction
There are two main problems with early direct instruction: a) students often do not have the necessary prior knowledge differentiation to be able to discern and understand the affordances of domain-specific representations and methods given during DI, b) when concepts, representations, and methods are presented in a well-assembled, structured manner during DI, students may not understand why those concepts, representations, and methods are assembled in the way that they are.
Four Core Mechanisms
Given these two problems, PF requires engaging students in a learning design that embodies four core interdependent mechanisms: (a) activation and differentiation of prior knowledge in relation to the targeted concepts, (b) attention to critical conceptual features of the targeted concepts, (c) explanation and elaboration of these features, and (d) organization and assembly of the critical conceptual features into the targeted concepts.
The PF Phases
The four core mechanisms are embodied in a design comprising two phases:
Design Principles
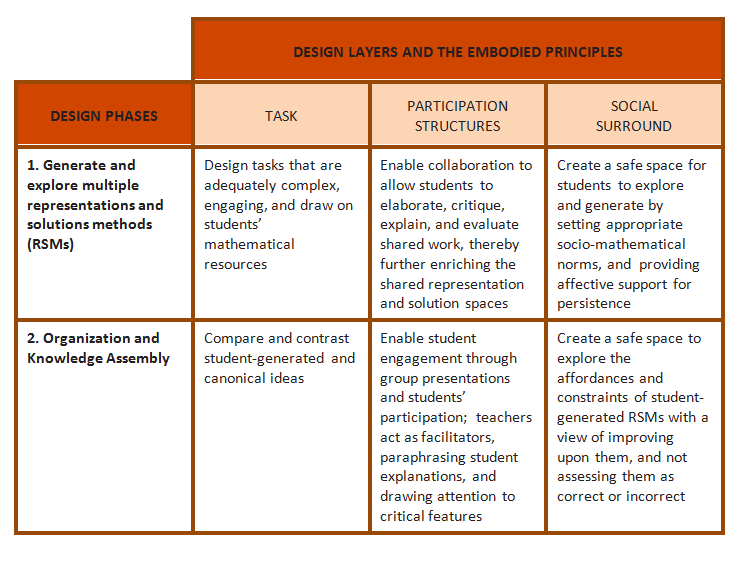
The designs of both phases involved decisions concerning the creation of the activities, the participation structures, and the social surround (see Table 1). These decisions were guided by the following core design principles to embody the aforementioned mechanisms:
1. Create problem-solving contexts that involve working on complex problems that challenge but do not frustrate, rely on prior mathematical resources, and admit multiple RSMs (mechanisms a and b).
2. Provide opportunities for explanation and elaboration (mechanisms b and c).
3. Provide opportunities to compare and contrast the affordances and constraints of failed or suboptimal RSMs and the assembly of canonical RSMs (mechanisms b–d).
Implementation of Core Design Principles
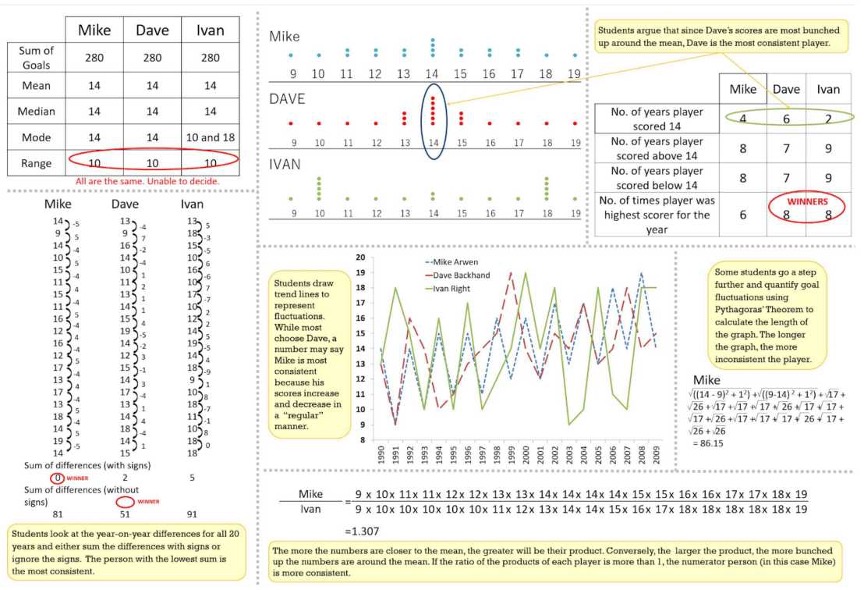
The following table is a summary of the ways in which these core principles have been implemented in the designs of the two phases (for a more detailed analysis, please refer to Kapur & Bielaczyc, 2011).